Electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular in modern society due to their efficiency, eco-friendliness and potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. But as more electric cars hit the roads, the need for efficient electric charging systems becomes greater.
Connector type is a key aspect when choosing a charging station, as different electric vehicle models may require different types of charging connectors. In general, if you delve into the technical characteristics of the charger or even the car itself, the names of the connectors can be confusing. Let’s figure out why there is such a variety of them, and what lies behind each of them. Go!
What types of charging stations are there?
You probably already know that there are home and commercial charging stations. But besides this, stations are divided into 2 types: AC and DC stations.
“Choosing between AC and DC stations is a choice between convenience for daily charging and high-speed power for long trips.” – Octa Energy
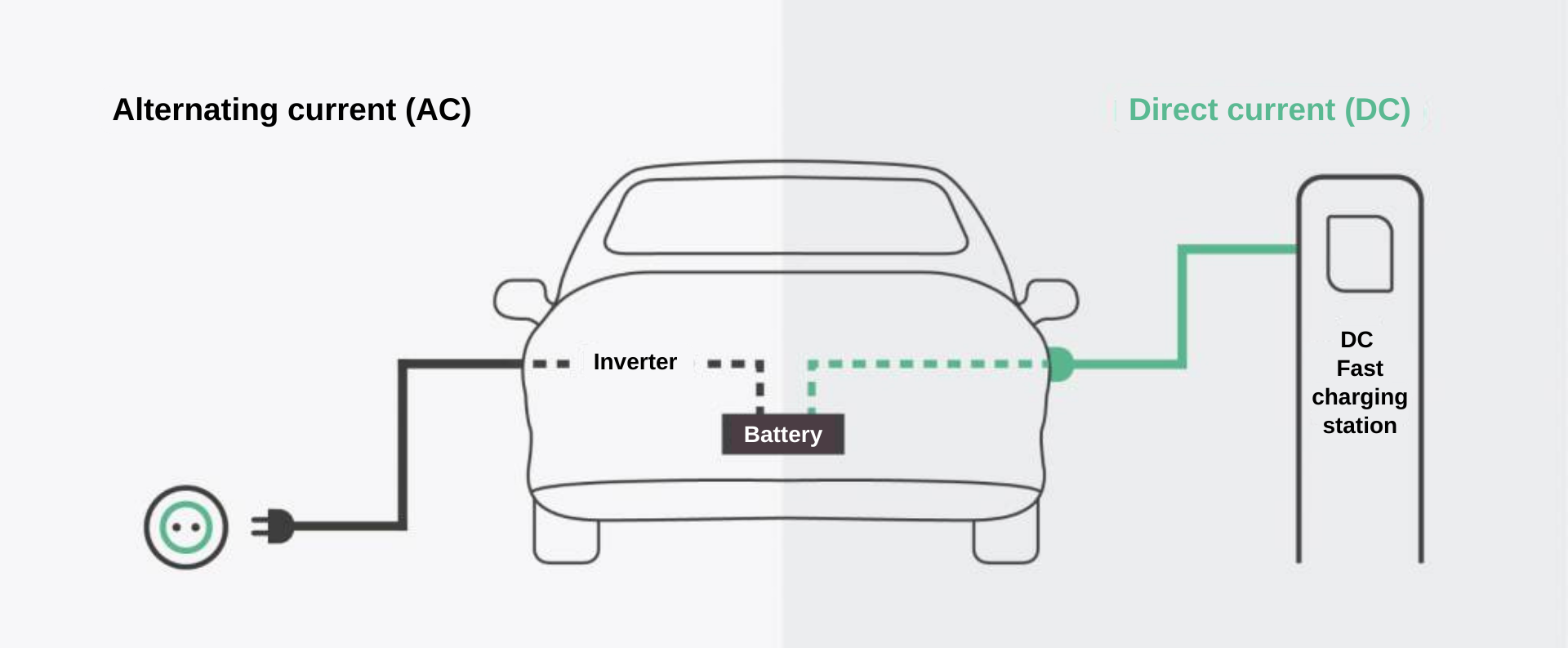
Alternating current (AC) stations
Electrical current from the station is supplied to the vehicle’s on-board converter, which then converts alternating current into direct current to charge the battery. This current conversion process reduces charging efficiency and speed. Therefore, AC charging stations usually offer slow charging and are ideal for home use or overnight charging.
Advantages:
- Low cost of installation and operation. AC stations cost less than DC and require less maintenance.
- Easy to install. AC stations are easy to install and can sometimes be connected to existing electrical networks without major modifications.
Flaws:
- Charging speed is slow.
- Inconvenient for long trips.
Direct current (DC) stations
In the case of DC charging stations, electrical current is supplied directly to the vehicle’s battery in the form of direct current, bypassing the on-board converter. This allows for significantly faster charging speeds as the process is not slowed down by current conversion and is optimized for maximum efficiency.
Therefore, DC charging stations offer high-speed charging, making them especially useful in commercial and public charging networks. They can charge most EV batteries up to 80% in just 20-30 minutes.
Advantages:
- High charging speed, which makes DC charging stations attractive for drivers over long distances.
- Efficiency. Due to charging speed, DC stations are usually more efficient in high traffic areas.
Flaws:
- High cost of installation and operation. DC stations require significant investment in installation and maintenance.
- High power consumption. High-speed chargers consume a lot of electricity, which can affect local power grids.
Both types of electric charging stations have their place in the electric car infrastructure and complement each other. Drivers simply choose between fast charging on the road and slow charging at home or work.
Main types of connectors
Type 1 (SAE J1772, J-Plug)
Standard connector for charging electric vehicles with alternating current in North America and Japan. The Type 1 connector can deliver up to 7.4kW of power, making it suitable for slow to moderate charging.
Compatibility:
- Chevrolet Volt;
- Nissan LEAF;
- New Toyota Prius models that support charging capabilities.
Type 2 (Mennekes)
The connector is designed for three-phase alternating current (AC) charging, and there is also the possibility of fast charging up to 22 kW. It has two additional contacts for three-phase charging, so it is more energy efficient and allows you to charge the car faster compared to the Type 1 connector.
The connector is mainly used for charging electric cars in Europe. Compatibility:
- Toyota;
- Nissan;
- Kia;
- Mitsubishi;
- Ford.
This connector is capable of supporting both standard charging up to 3.7 kW and accelerated charging up to 22 kW.
CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is an acronym for Charge de Move. This DC fast charging system was developed in Japan. It supports very high charging capabilities as well as bi-directional charging. Typically this connector provides power up to 100 kW, however revised specifications allow power up to 400 kW (1000 V, 400 A).
Compatibility:
- Nissan Leaf,
- Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV,
- Toyota Prius Plug-In,
- Citroen C-Zero,
- Citroen Berlingo Electric Mk1 and others.
The CHAdeMO standard is widely used in Japan, Europe and North America. Very often, public electric charging stations have CHAdeMO connectors for fast charging.
CCS Combo
CCS Combo, or Combined Charging System (combined charging system) combines variable and constant charging current in one connector, which makes it a convenient and flexible solution for charging electric car batteries. There are two versions of this connector: Combo 1 (common in the US) and Combo 2 (common in Europe).
The standard supports up to 350 kW DC power, making it one of the fastest charging standards.
Compatibility:
- BMW i3,
- VW e-Golf,
- Tesla Model 3 (for the European market),
- Audi,
- Ford,
- Mercedes,
- Renault
- Volvo and others.
Tesla Supercharger
Tesla has developed its own charging connector standard that allows vehicles to be charged on both DC and AC power through a single connector.
The Tesla Supercharger connector transmits high power, up to 250 kW, which allows drivers to charge their car very quickly – up to 80% in just half an hour.
Tesla is actively expanding its Supercharger network around the world, providing good coverage in North America, Europe and Asia.
Compatibility. Supercharger connectors are designed exclusively for Tesla vehicles, making them incompatible with other brands of electric vehicles without special adapters.
GB/T (Guobiao Standard)
GB/T is a standard created in China for electric vehicle charging systems that is used domestically and supports both DC and AC charging. The throughput power of the connector reaches 900 kW, which allows you to quickly charge an electric vehicle.
Compatibility. The GB/T connector is only compatible with vehicles manufactured in China. For example, electric cars from manufacturers:
- BYD;
- NIO;
- Great Wall Motors;
- Li Auto.
Cars from European or American manufacturers that are made exclusively for China are also necessarily compatible with this connector. This is due to the requirements of Chinese standards for electric vehicles and charging infrastructure. For example:
- Tesla;
- Nissan;
- Renault;
- Chevrolet;
- Ford and others.
Therefore, if a European or American brand vehicle is sold in China, it will usually be equipped with a GB/T connector to comply with local regulations and ensure compatibility with the national charging network.
Choosing the right charging connector depends on many factors, including the type of electric vehicle you own, your geographic location, and the availability of charging stations. Understanding these differences will help ensure efficient and convenient charging, increasing your driving range and overall satisfaction.
Choosing the right charging connector depends on many factors, including the type of electric vehicle you own, your geographic location, and the availability of charging stations. Understanding these differences will help ensure efficient and convenient charging, increasing your driving range and overall satisfaction.
“Charging becomes a simple task when you choose a connector that is compatible with your electric vehicle. We recommend choosing one that matches your vehicle and your location’s standards, and provides efficient charging speeds.” – Octa Energy