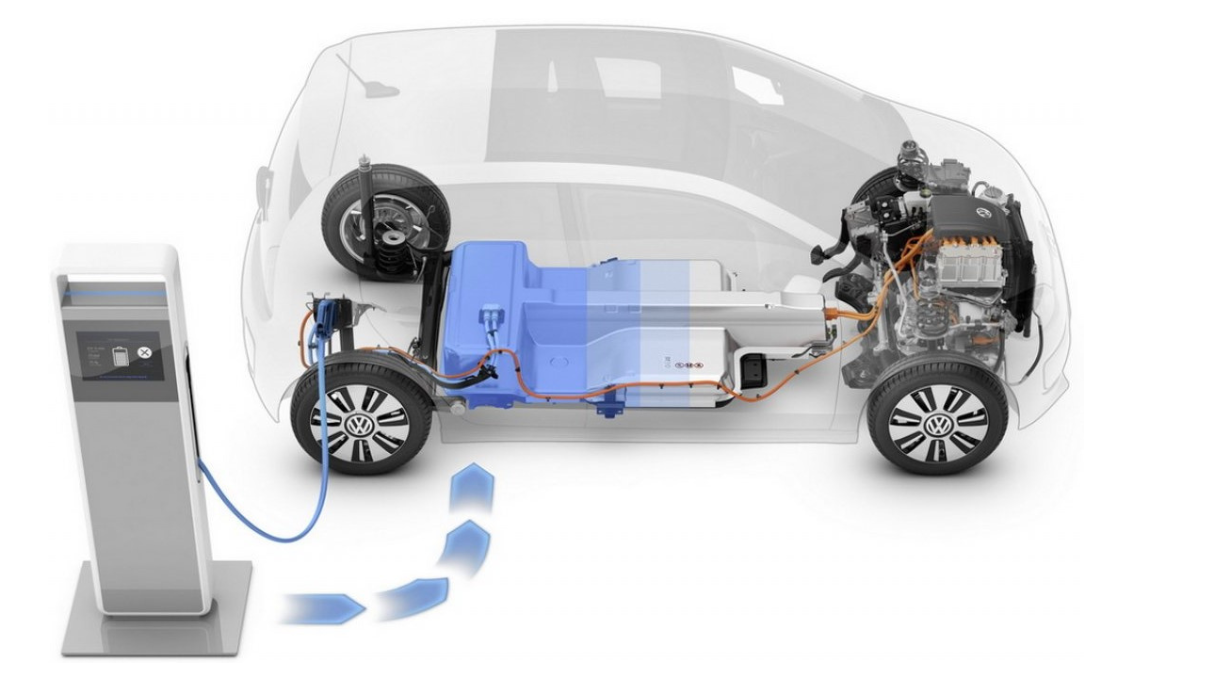
Electric vehicles are an innovative trend in the automotive industry based on the use of electric power for propulsion. The key component of an electric vehicle is its batteries, which determine its efficiency and range. Currently, there are several types of batteries used in electric vehicles. Each has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, making the selection of an electric vehicle battery an important step in the production and use of electronic vehicles.
“The choice of battery type for an electric vehicle depends on various factors such as range, cost, safety and environmental aspects.” – Octa Energy
Lithium-ion batteries
One of the most common and promising types of batteries used in electric vehicles are lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion). This type of battery deserves special attention because it has superior characteristics compared to alternative technologies.
These batteries are known for their high energy density and relatively low weight, which allows for greater range on a single charge. Lithium-ion batteries are most often produced using lithium as the active element, which allows for efficient ion exchange.
Advantages:
- long service life;
- fast charging capability.
Flaws:
- production cost is quite high;
- do not have resistance to high and low temperatures.
Among the main varieties the following can be distinguished.
Lithium-cobalt
They have a high energy density, making them ideal for long-range electric vehicles such as the Tesla Model S. However, due to their limited charge-discharge cycle, their use is limited to high-performance vehicles.
Lithium iron phosphate
They are distinguished by increased safety and durability, but have a slight decrease in energy density. They are often used in electric vehicles where safety is key, such as the BYD e6.
Lithium manganese
They have high stability and efficiency under conditions of increased technological consumption. Therefore, they are suitable for energy-intensive electric vehicles, for example the Chevrolet Volt.
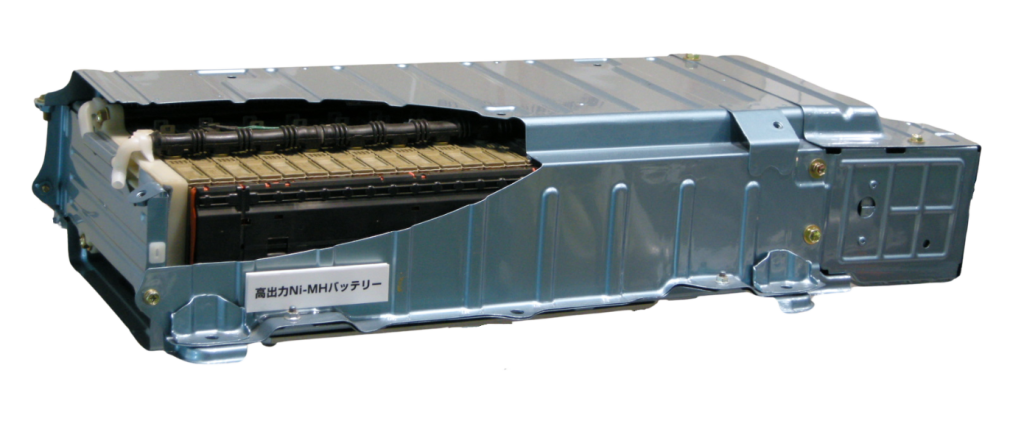
Nickel-metal hydride batteries
Another option used in electric vehicles is nickel metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. They differ from lithium-ion batteries by using nickel as the active element. This type provides good energy density and does not contain harmful materials such as cobalt, so it is more environmentally friendly. Some models, such as the Toyota Prius, use this type of battery.
Advantages:
- relatively low cost;
- safety in operation;
- simpler production technology.
Flaws:
- low energy density;
- more limited fast charging options;
- shorter service life.
Lead-acid batteries
Although less common in electric vehicles, lead-acid (SLA) batteries are still used in some models. This type of battery has a low energy density, but is characterized by a long service life and relatively low cost. However, their weight and dimensions may be unacceptable for some electric vehicle designs.
Solid-state batteries
Recently, solid-state batteries have also been actively researched and developed. They differ in what they are made of – instead of a liquid electrolyte, a solid material is used. This gives these batteries greater safety, stability and a long service life. Solid-state batteries also have the potential to increase energy density and resistance to overheating. However, they are currently expensive to produce and their use in electric vehicles is limited.
Where batteries for electric vehicles are made also plays an important role. Many of them are produced in countries with developed automotive industries, such as China, the USA, Germany and Japan. These countries have advanced technology and production capacity, which contributes to the high quality and innovation of the batteries produced.
Each of the mentioned battery types has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the car manufacturer. For example, Tesla makes extensive use of lithium-ion batteries in its models in an effort to maximize range and performance. Toyota, for its part, is focusing on nickel-metal hydride batteries in its hybrid models, with an emphasis on sustainability and environmental friendliness.
“With advancements in technology and research, the future of electric vehicles promises new standards in safety, energy efficiency and sustainability.” – Octa Energy