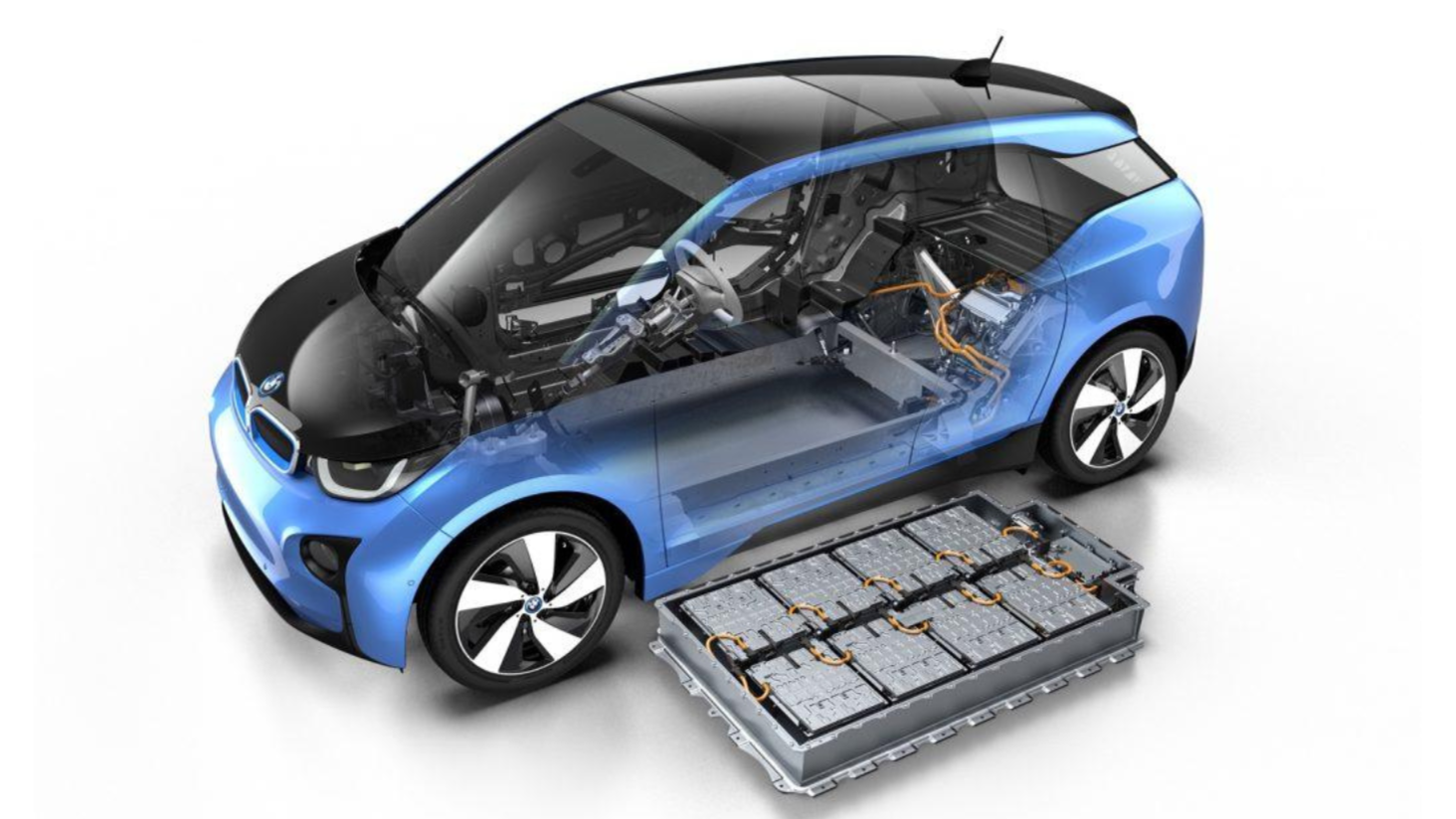
Electric vehicle batteries are highly efficient lithium-ion batteries that provide the electric vehicle with the energy to move. They consist of several individual cells containing an electrolyte and carbon anodes. Lithium, due to its high electrical conductivity, plays a key role in ensuring efficient energy transfer in these batteries.
The benefits of using batteries in electric vehicles include zero emissions and more efficient energy use compared to traditional fuel systems. But users continue to be concerned with the question: how many years will the battery life last for comfortable use of an electric vehicle?
“The future belongs to those who see the electric vehicle battery as not just a source of energy, but a path to modern capabilities.” – Octa Energy
How long do batteries last in electric cars?
Thanks to modern technologies, automakers have been able to significantly reduce the rate at which batteries lose capacity. The average battery life of electric vehicles varies from 8 to 15 years depending on the model and manufacturer. This is the period during which the batteries remain suitable to provide the required capacity.
- Tesla car batteries are considered among the most reliable on the market and can maintain high capacity for more than 10 years. Tesla Model S loses only about 2% of capacity per year over an average range of 15 to 20 thousand kilometers under various operating conditions, including cold and heat, intense driving and fast charging.
- The Nissan Leaf electric car, which is quite popular, shows a loss of approximately 4-4.5% of capacity per year. This is important given the low power reserve of the car, and after 7-10 years the battery may need to be replaced for normal use of the car, which is also a competitive indicator.
Why are electric vehicle batteries gradually running out of capacity?
Over time, the active materials inside batteries undergo chemical reactions and physical changes, resulting in loss of capacity. The electrodes gradually form a film that reduces the batteries’ ability to hold a charge. The following factors also affect battery life.
- High temperatures. Heat and overheating can speed up the aging process of batteries. At high temperatures, electrolyte cells begin to lose their ability to hold current.
- Discharge-charge cycle. Electric vehicle batteries undergo a constant discharge-charge cycle, which ultimately affects their capacity. In each cycle, a chemical reaction occurs, and, despite modern technology, it leaves its mark.
- Fast charging. The increase in temperature inside the battery and wear and tear on the electrochemical system with each rapid charge leads to a gradual decrease in capacity. Therefore, you should use fast charging only when necessary.
- Mechanical damage. The sealed battery capacity can be severely damaged by mechanical damage. How and when such damage manifests itself depends on the specific situation.
It is worth emphasizing that it is important to use only original or certified chargers, which are Octa. Cheap or homemade devices can cause battery failure due to voltage fluctuations.
Electric vehicle batteries are undoubtedly a key element for a sustainable future of transport. Despite the limited resource, ongoing research and development is aimed at increasing the capacity and extending the life of batteries, making electric vehicles even more attractive for mass use.
“EV batteries are the key to a future where every charge opens the door to a sustainable tomorrow.” – Octa Energy